Raising and Handling for Ginger
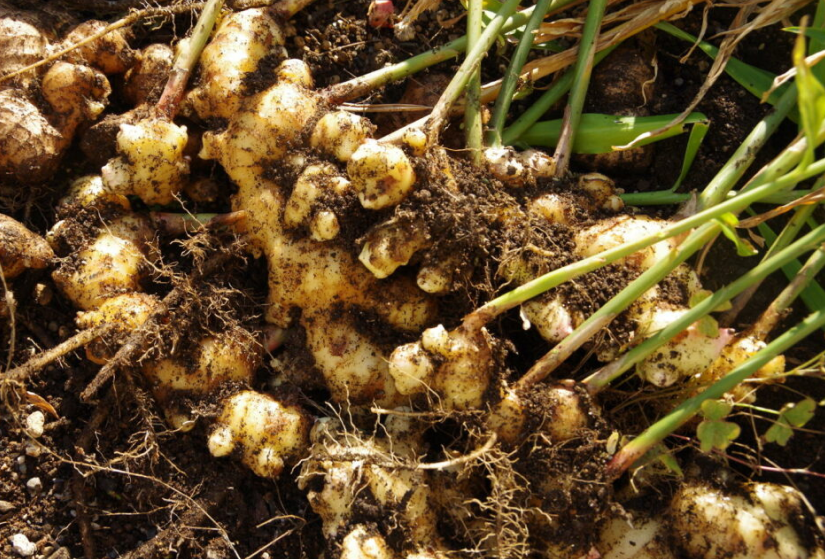
Ginger, is a herbaceous perennial from Asia, where it is commercially farmed. The edible component of the herb is the plump, knobbly, subterranean rhizome, which is one of the world's most popular spices. Although the branches can develop flowers, they aren't regarded as decorative, and container plants seldom blossom. If you reside in warmer locations, you may be capable of growing ginger outside, otherwise grow it in pots and bring it inside when the weather cools. It doesn't grow quickly, taking around eight to ten months from seeding in early spring to harvesting the rhizome.
Characteristics

Mature Size
Up to 120 cm tall, 60 cm wide
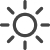
Sun Exposure
Full sun, partial shade

Soil Type
Well-drained, moist, rich

Soil pH
Neutral

Bloom Time
Fall

veg. color
Yellow, cream, green
Environmental Footprint
Varieties and differences
Galangal is the common name for several types of ginger, including Thai ginger, Finger root, Chinese Keys, and Tropical ginger. It tastes sweeter and far less pungent than regular ginger and is frequently marketed frozen or pickled.
Turmeric is also one of the ginger varieties that has been used for over 5,000 years throughout Southern Asia. When dried or cooked, its vivid orange interior turns a unique shade of yellow.
The peacock ginger plant has stunning purple blossoms and grows barely a few inches above the ground. The plant may appear attractive and decorative, but it has a variety of medical and aesthetic applications.
Fertilizer
If you don’t put your ginger root in especially fertile soil, you’ll need to use a lot of fertilizer to get a good harvest these seedlings are heavy feeders. A gradual, all-purpose fertilizer rich in phosphorus applied once in spring and early summer, together with a monthly dose of liquid fertilizer, should yield good results. Some gardeners also add compost throughout the summer. If you get a lot of rain, watering every few days may be essential to replenish nutrients that leak from the soil.
Soil
The ginger root grows best on loamy soil that is rich, well-drained and retains moisture. Although it may thrive in slightly acidic environments, the plant favors neutral pH.
Water
Waterlogged soil is the last thing you want while growing ginger. However you should hydrate the plant thoroughly and frequently during the growing season, generally at least 2.5 cm each week, you should be careful not to overwater it. Root rot can occur in wet environments.
Light
Ginger root grows best in full or partial sun. Filtered sunlight is ideal for southern locations that face extreme heat.

Humidity and temperature
Outdoors, optimum soil conditions for growing ginger are approximately 25 degrees. However, provided the plant is shielded from strong winds, temperatures ranging from 18 to 24 degrees Celsius may result in a robust yield. If temperatures fall under 18 degrees, the plant may go into dormancy, and if the temperature drops beneath 10 degrees Celsius, bring it indoors.
Harvesting
To grow ginger outside, you’ll need hot, humid weather and nutrient-rich soil. Crop rotation also will boost the likelihood of a plentiful and healthy crop. So, attempt to plant one every few years to avoid disease and insect concerns.
If you can’t ensure tropical-type outside temps, cultivate your ginger root in pots and move them inside when the colder weather arrives.
Recipe Description
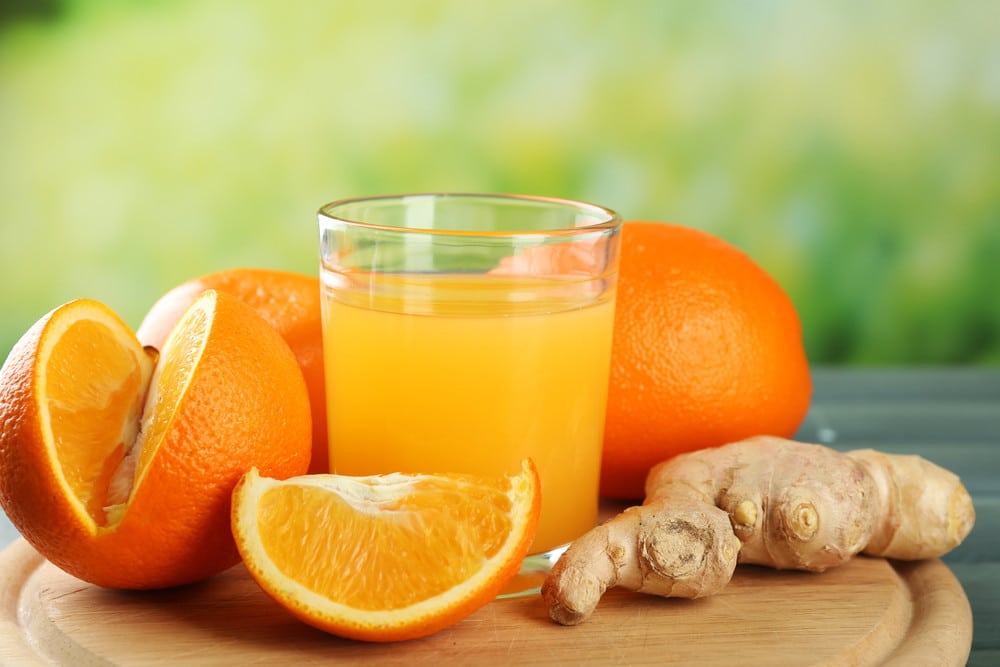

Detox Drink with Orange and Ginger
Ingredients
- 1 medium carrot
- Two oranges
- 1 raw turmeric (crushed)
- 1 ginger (crushed)
- 1/2 Lemon (juiced)

Servings
2 people

Prepping time
15 min

Cooking time
0 min
- Separately juice the orange and carrot.
- In a blender, combine the juice with turmeric and ginger.
- Mix for 30 seconds before squeezing half a lemon.
- Serve with a strainer.
Order Plant Food in our Shop!
Shop NowFAQ
What is the distinction between ginger root and blooming ginger?
How easy is it to care for ginger root?
If you have warm weather and well-drained soil, you should be able to harvest an abundance of ginger roots with little effort.